
FFA
FFA
Hearing problems affect millions of people worldwide, impacting their quality of life and communication abilities. At FFA, we are committed to raising awareness, providing support, and promoting solutions for those experiencing hearing loss. This guide is designed to help you understand the different types of hearing problems, their causes, and the available treatments.
Types of Hearing Problems
- Definition : Occurs when sounds cannot pass through the outer and middle ear.
- Causes : Ear infections, fluid in the middle ear, earwax buildup, or damage to the ear canal.
- Treatment : Medical or surgical interventions, such as removing earwax or treating infections.
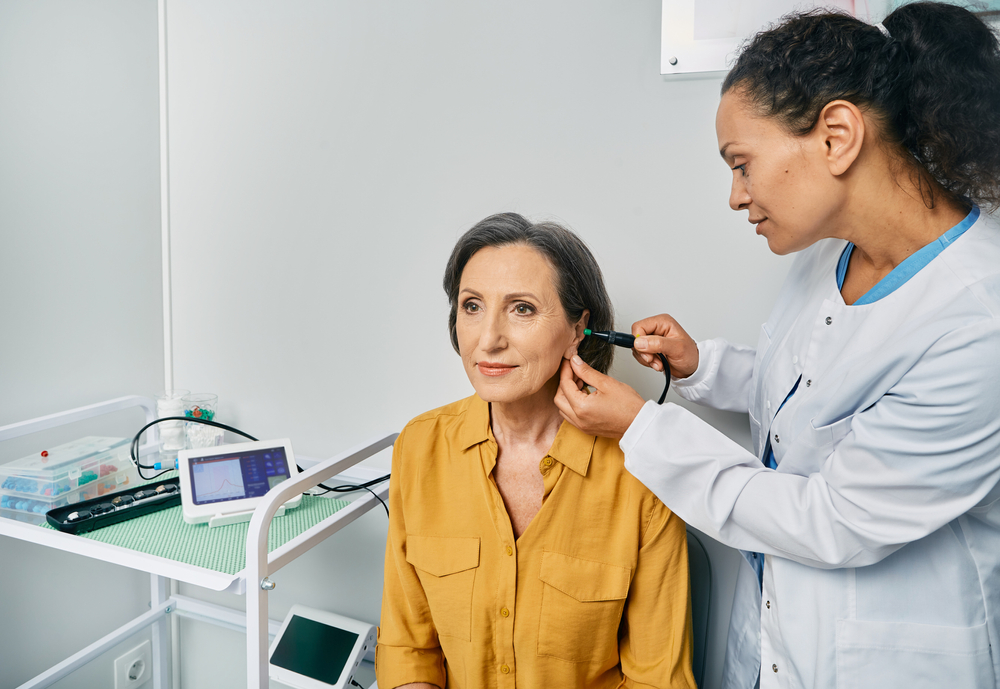
- Pediatric Audiology : FFA is invaluable in diagnosing congenital hearing loss, allowing audiologists to implement early treatment plans.
- Causes : Aging, exposure to loud noise, genetic factors, or head trauma.
- Treatment : Hearing aids, cochlear implants, and assistive listening devices.
Conductive Hearing Loss
- Definition : A combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.
- Causes : Conditions that affect both the outer/middle ear and the inner ear or auditory nerve.
- Treatment : A combination of medical treatments and hearing devices.
Mixed Hearing Loss
- Definition : Difficulty in processing sounds, despite normal hearing ability.
- Causes : Often developmental, but can also result from brain injury.
- Treatment : Auditory training and use of assistive listening devices.
Auditory Processing Disorders
Causes of Hearing Problems
- Aging : Natural wear and tear on the ear structures over time.
- Noise Exposure : Prolonged exposure to loud noises from music, machinery, or explosions.
- Infections : Chronic ear infections can lead to permanent damage.
- Genetics : Hereditary factors can predispose individuals to hearing loss.
- Ototoxic Medications : Some medications can damage the ear structures.
- Physical Trauma : Injuries to the head or ear can cause hearing loss.
